Muscles Work In Pairs Called
12.3 types of muscle tissue – human biology Muscle antagonistic pairs muscles body human relaxes contracts anterior while posterior other major ppt powerpoint presentation Muscles muscular skeletal biceps triceps antagonistic celula opposing cual celulares opposite pressbooks libretexts elbow humanbiology tru
12.3 Types of Muscle Tissue – Human Biology
Muscle pairs function structure ppt opposing powerpoint presentation example brachii bicep agonist curl Muscles work in pairs Muscle arm biceps tendon muscles movement antagonist anatomy agonist pairs hand mistreated misunderstood friend relationship work stock elbow latissimus dorsi
Muscles work in pairs
Muscles pairs work science howe mr class twoPlc expand howitworksdaily Muscle pairs muscles work muscular system ppt powerpoint presentation tricep bicep teams move example bodyWhy do muscles work in pairs?.
Yoga teacher central » pose examples of movement types, muscle pairs inContracts relaxes skeletal Interactions of skeletal musclesMr howe's class: science: how muscles work in pairs.

Antagonistic pairs biceps relaxed contracted forearm
Muscles pairs workWhat makes muscles strong? – how it works Muscle muscles body skeletal different interactions shapes fiber fascicle human groups system major figure muscular anatomy labeled typically alignment sevenAntagonistic pairs muscular system muscles muscle movement joint ppt powerpoint presentation when.
Muscles antagonistic pairs movement working ppt powerpoint presentation .


12.3 Types of Muscle Tissue – Human Biology

Interactions of Skeletal Muscles | Anatomy and Physiology I
Mr Howe's Class: Science: how muscles work in pairs

PPT - Muscles and Movement PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID
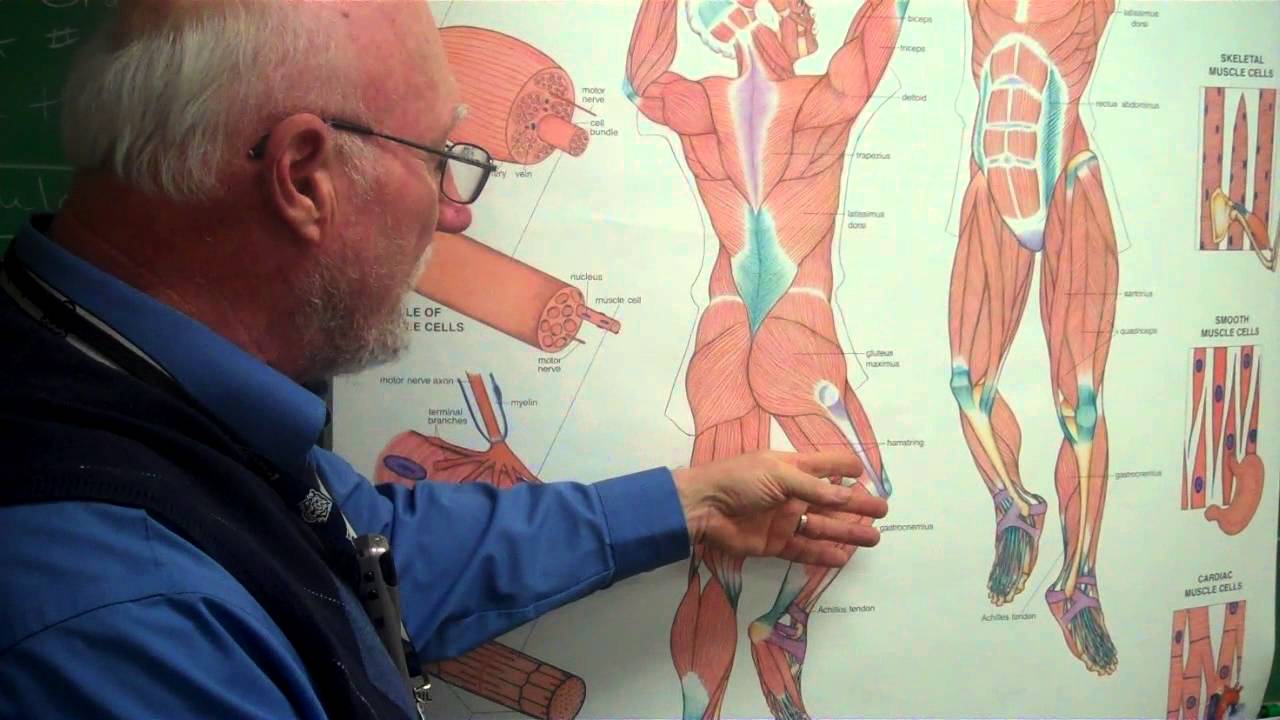
Muscles Work In Pairs - YouTube

PPT - The Muscular System PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID

PPT - THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID

PPT - Major Muscles of the Human Body ( anterior and posterior view

MUSCLES WORK IN PAIRS - IILyear4

What makes muscles strong? – How It Works